public class LifeCycleTest extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "ActivityLifeTest";
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Log.v(TAG, "onCreate");
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&saddr=startLat%20startLng&daddr=endLat%20endLng&hl=en");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(it);
}
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.v(TAG, "onStart");
}
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.v(TAG, "onResume");
}
public void onPause() {
super.onPause();
Log.v(TAG, "onPause");
}
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
Log.v(TAG, "onStop");
}
public void onRestart() {
super.onRestart();
Log.v(TAG, "onReStart");
}
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.v(TAG, "onDestroy");
}
}
First, new a project with Google APIs.
Then, Run it.
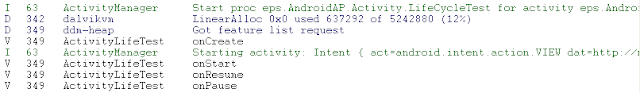
We can see that Log:ActivityLifeTest is onPause now. It means the Intent start another Activity.
If we press “BACK”, Activity:LifeCycleTest will resume again.
Now, restart the Activity, and press “Maps”.
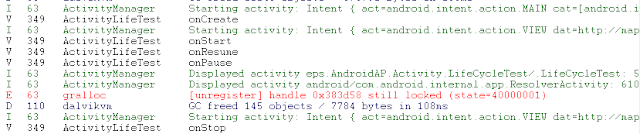
We can find out that Activity:LifeCycleTest is stopped. It means Activity:LifeCycleTest is no longer visible.
Finally, press “BACK” to the Activity:LifeCycleTest, and Activity:LifeCycleTest will restart.
If we leave the Activity:LifeCycleTest, Activity:LifeCycleTest will be destroyed.
Reference:
http://stenlyho.blogspot.com/search/label/Android
http://code.google.com/p/androidbmi/wiki/LifeCycle
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-TW/guide/topics/fundamentals.html
üW
üWe






沒有留言:
張貼留言